TS Cheat Sheet
为什么写这篇
antfu的题目 大多就是基础方法+递归, issues充斥着重复内容, 最开始还有点TS的味道, 后面完全变成了只有基础方法, 组合出一个东西, 感觉这个更适合作为递归练习题, 而不是TS练习题 (没有数值强行用数组拼接+length, 等等
TS有文档,是英文的,难以用中文检索
本篇呢,是cheatsheet,不是document,把实际会用到常用的一些列出来+一些场景描述
内容
官方文档
TS默认类型
范围控制 通过各种if让一个范围内 的类型被自动推断
函数
对象
Generic 通用类型
Conditional Types
Mapped Types
模板字面类型
类
modules
工具
playground
ts-toolbelt
utility-types
自定义类型名
1
| type HelloWorld = string
|
有默认值的参数
1
| type HelloWord<T,W = 默认值>
|
数组内容的类型Union
T是数组类型
对象
空对象
对象里面, 父类的required key不比子类多, 且对应的是public
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| type p0 = {} extends {}?true:false
type p1 = {} extends {x?:3}?true:false
type p2 = {} extends {x:3}?true:false
type p3 = {x:3} extends {}?true:false
|
条件类型
Conditional Types
相当于引入了if逻辑, 有了这个你可以自定义很多默认未提供的操作符, 并且可以递归的定义
注意的是 T 如果是Union类型, 会分别对Union的每一个进行校验, 见 distributive-conditional-types
为了防止 Union 被拆散 可以套一层括号
1
2
3
| type W<T> = T extends never ? never : [T]
type K = W<1|2>
|
U 可以是单独类型/数值/字符串,联合类型, 甚至
1
| `${'a' | 'b'}${infer R}`
|
而且这似乎在+?,-?,-readonly,+readonly上没法用,还要拆开再合并
注意+? 会让类型多|undefined,-? 会去掉undefined, 所以对对象 Required<Partial<Type>> 操作, undefined 会变never
在条件中提取未知的具体类型
inferring-within-conditional-types
1
| type Flatten<Type> = Type extends Array<infer XXX> ? XXX : Type;
|
递归例子
1
| W<T extends S<any>> = T extends S<infer U> ? (U extends S<any> ? W<U> : U) : never
|
可以递归提取数组, 对象值, 函数参数, 函数返回值
1
| type Includes<T extends readonly any[], U> = T extends [infer A, ...infer R] ? (Equal<A, U> extends true ? true : Includes<R, U>) : false
|
函数参数类型 union 的提取
1
2
3
| type Y = ((x: {y:3}) => any) | ((z: {w:4}) => any)
type X = Y extends (x: infer V) => any ? V : never
|
Union
合并两个类型, 并让类型自动区别具体是哪个, 例如接口成功返回字段和失败返回字段不一样
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| interface SuccessResp{
status: 0;
value: string;
}
interface ErrorResp{
status: 'error';
message: string;
}
type Resp = SuccessResp | ErrorResp
const r: Readonly<Resp> = api.xxx(...);
if (r.status == 'error'){
}else{
}
|
获取一个对象的所有键的字符串Union
Keyof Type Operator
有了这个你可以去对对象键操作做校验
1
2
3
| type Point = { x: number; y: number };
type P = keyof Point;
|
同理获得对象所有值的Union
1
2
3
| type Point = { x: number; y: number };
type P = Point[keyof Point];
|
同值类型不同键名
Record<Keys, Type>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| interface CatInfo {
age: number;
breed: string;
}
type CatName = "miffy" | "boris" | "mordred";
const cats: Record<CatName, CatInfo> = {
miffy: { age: 10, breed: "Persian" },
boris: { age: 5, breed: "Maine Coon" },
mordred: { age: 16, breed: "British Shorthair" },
};
|
字段相关工具 Pick / Omit / Mapped Types
字段相关工具
Utility Types
从已有的类型中取其中部分字段建立新类型
Pick<Type, Keys>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| interface Todo {
title: string;
description: string;
completed: boolean;
}
type TodoPreview = Pick<Todo, "title" | "completed">;
|
从已有的类型中移除部分字段建立新类型
Omit<Type, Keys>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| interface Todo {
title: string;
description: string;
completed: boolean;
createdAt: number;
}
type TodoPreview = Omit<Todo, "description">;
|
自定义需要哪些键, 从哪个Type中取, 甚至做一些去除 ?, 键名重定义as的操作(可以as到never 消除这个键)
Mapped Types
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| type Getters<Type> = {
[Property in keyof Type as `get${Capitalize<string & Property>}`]: () => Type[Property]
};
interface Person {
name: string;
age: number;
location: string;
}
type LazyPerson = Getters<Person>;
|
更新对象部分内容时
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| interface Todo {
title: string;
description: string;
}
function updateTodo(todo: Todo, fieldsToUpdate: Partial<Todo>) {
return { ...todo, ...fieldsToUpdate };
}
const todo1 = {
title: "organize desk",
description: "clear clutter",
};
const todo2 = updateTodo(todo1, {
description: "throw out trash",
});
|
Equal
StackOverflow How to test if two types are exactly the same
1
2
3
| type IfEquals<T, U, Y=unknown, N=never> =
(<G>() => G extends T ? 1 : 2) extends
(<G>() => G extends U ? 1 : 2) ? Y : N;
|
只读
只有首次赋值, 不能修改, 和freeze一样,不影响二级的内容,只是顶级的内容
1
| function freeze<Type>(obj: Type): Readonly<Type>;
|
Readonly
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| interface Todo {
title: string;
}
const todo: Readonly<Todo> = {
title: "Delete inactive users",
};
|
从Union Type中去掉指定的一些Type
Exclude<UnionType, ExcludedMembers>
1
| Exclude<UnionType, ExcludedMembers>
|
1
2
| type T0 = Exclude<"a" | "b" | "c", "a">;
|
函数 参数数组 / 返回类型
参数数组
Parameters
1
2
| type T1 = Parameters<(s: string) => void>;
|
构造函数参数
ConstructorParameters
1
| ConstructorParameters<Type>
|
函数返回类型
ReturnType
1
2
| type T0 = ReturnType<() => string>;
|
this 标注
指定方法中/对象中的的this的字段, it serves as a marker for a contextual this type. Note that the noImplicitThis flag must be enabled to use this utility.
ThisType
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| type ObjectDescriptor<D, M> = {
data?: D;
methods?: M & ThisType<D & M>;
};
function makeObject<D, M>(desc: ObjectDescriptor<D, M>): D & M {
let data: object = desc.data || {};
let methods: object = desc.methods || {};
return { ...data, ...methods } as D & M;
}
let obj = makeObject({
data: { x: 0, y: 0 },
methods: {
moveBy(dx: number, dy: number) {
this.x += dx;
this.y += dy;
},
},
});
obj.x = 10;
obj.y = 20;
obj.moveBy(5, 5);
|
移除Type的this参数。如果Type没有明确声明的this参数,结果只是Type。否则,一个没有this参数的新函数类型将从Type创建。泛型被擦除,只有最后的重载签名被传播到新的函数类型。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| function toHex(this: Number) {
return this.toString(16);
}
const fiveToHex: OmitThisParameter<typeof toHex> = toHex.bind(5);
console.log(fiveToHex());
|
装饰器Decorators
Decorators
比官方还详细的指南
类装饰器, target 是类的构造器, 返回新的构造器
例如我们可以添加一个toString方法给所有的类来覆盖它原有的toString方法。
1
2
| type ClassDecorator = <TFunction extends Function>
(target: TFunction) => TFunction | void;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| type Consturctor = { new (...args: any[]): any };
function toString<T extends Consturctor>(BaseClass: T) {
return class extends BaseClass {
toString() {
return JSON.stringify(this);
}
};
}
@toString
class C {
public foo = "foo";
public num = 24;
}
console.log(new C().toString())
|
装饰器并没有类型保护,这意味着:issues 4881
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| declare function Blah<T>(target: T): T & {foo: number}
@Blah
class Foo {
bar() {
return this.foo;
}
}
new Foo().foo;
|
解决方案
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| declare function Blah<T>(target: T): T & {foo: number}
class Base {
foo: number;
}
@Blah
class Foo extends Base {
bar() {
return this.foo;
}
}
new Foo().foo;
|
属性装饰器
target: 对于静态成员来说是类的构造器,对于实例成员来说是类的原型链。
propertyKey: 属性的名称
除了用于收集信息外,属性装饰器也可以用来给类添加额外的方法和属性。 例如我们可以写一个装饰器来给某些属性添加监听器。
1
2
| type PropertyDecorator =
(target: Object, propertyKey: string | symbol) => void;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| function capitalizeFirstLetter(str: string) {
return str.charAt(0).toUpperCase() + str.slice(1);
}
function observable(target: any, key: string): any {
const targetKey = "on" + capitalizeFirstLetter(key) + "Change";
target[targetKey] =
function (fn: (prev: any, next: any) => void) {
let prev = this[key];
Reflect.defineProperty(this, key, {
set(next) {
fn(prev, next);
prev = next;
}
})
};
}
class C {
@observable
foo = -1;
@observable
bar = "bar";
}
const c = new C();
c.onFooChange((prev, next) => console.log(`prev: ${prev}, next: ${next}`))
c.onBarChange((prev, next) => console.log(`prev: ${prev}, next: ${next}`))
c.foo = 100;
c.foo = -3.14;
c.bar = "baz";
c.bar = "sing";
|
方法装饰器
target: 对于静态成员来说是类的构造器,对于实例成员来说是类的原型链。
propertyKey: 属性的名称。
descriptor: 属性的描述器。
返回: 如果返回了值,它会被用于替代属性的描述器。
方法装饰器不同于属性装饰器的地方在于descriptor参数。 通过这个参数我们可以修改方法原本的实现,添加一些共用逻辑。 例如我们可以给一些方法添加打印输入与输出的能力:
1
2
3
4
5
| type MethodDecorator = <T>(
target: Object,
propertyKey: string | symbol,
descriptor: TypedPropertyDescriptor<T>
) => TypedPropertyDescriptor<T> | void;
|
访问器装饰器
访问器装饰器总体上讲和方法装饰器很接近,唯一的区别在于描述器中有的key不同:
方法装饰器的描述器的key为:
value
writable
enumerable
configurable
访问器装饰器的描述器的key为:
get
set
enumerable
configurable
例如,我们可以将某个属性的赋值 改为 展开拷贝:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| function immutable(target: any, propertyKey: string, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor) {
const original = descriptor.set;
descriptor.set = function (value: any) {
return original.call(this, { ...value })
}
}
class C {
private _point = { x: 0, y: 0 }
@immutable
set point(value: { x: number, y: number }) {
this._point = value;
}
get point() {
return this._point;
}
}
const c = new C();
const point = { x: 1, y: 1 }
c.point = point;
console.log(c.point === point)
|
参数装饰器
1
2
3
4
5
| type ParameterDecorator = (
target: Object,
propertyKey: string | symbol,
parameterIndex: number
) => void;
|
target: 对于静态成员来说是类的构造器,对于实例成员来说是类的原型链。
propertyKey: 属性的名称(注意是方法的名称,而不是参数的名称)。
parameterIndex: 参数在方法中所处的位置的下标。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| function f(key: string): any {
console.log("evaluate: ", key);
return function () {
console.log("call: ", key);
};
}
@f("Class Decorator")
class C {
@f("Static Property")
static prop?: number;
@f("Static Method")
static method(@f("Static Method Parameter") foo) {}
constructor(@f("Constructor Parameter") foo) {}
@f("Instance Method")
method(@f("Instance Method Parameter") foo) {}
@f("Instance Property")
prop?: number;
}
|
顺序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| evaluate: Instance Method
evaluate: Instance Method Parameter
call: Instance Method Parameter
call: Instance Method
evaluate: Instance Property
call: Instance Property
evaluate: Static Property
call: Static Property
evaluate: Static Method
evaluate: Static Method Parameter
call: Static Method Parameter
call: Static Method
evaluate: Class Decorator
evaluate: Constructor Parameter
call: Constructor Parameter
call: Class Decorator
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| function f(key: string) {
console.log("evaluate: ", key);
return function () {
console.log("call: ", key);
};
}
class C {
@f("Outer Method")
@f("Inner Method")
method() {}
}
|
1
2
3
4
| evaluate: Outer Method
evaluate: Inner Method
call: Inner Method
call: Outer Method
|
艹 Any,unknown,object,void,undefined,null,never
Any,unknown,object,void,undefined,null, and never assignability
字符串 大小写,首字母
Intrinsic String Manipulation Types
1
2
3
4
| Uppercase<StringType>
Lowercase<StringType>
Capitalize<StringType>
Uncapitalize<StringType>
|
Union 转 &
Generics + Union => ((x:U0)=>void) | ((x:U1)=>void) | ((x:U2)=>void) …
extends + infer => U0 & U1 & U2
注意的是有不少基础类型的&会是never, 做成函数或对象, 不会有这个问题,
同时基础值还可以通过 (A | B | D) & (A | C |D) 得到A|D
合并多个 &
可以完成新对象生成
1
2
3
| type Copy<T> = {
[K in keyof T]:T[K]
}
|
直接写和写template 不一致的情况
StackOverflow Why does Typescript Union + Mapped Types work differently with and without Generics
Distributive Conditional Types
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| type NodeA = {
type: 'A'
name: string
flag: number
}
type NodeB = {
type: 'B'
id: number
flag: number
}
type Nodes = NodeA | NodeB
type w0 = {
[k in keyof Nodes]: Nodes[k]
}
type Calc<W> = {
[k in keyof W]: W[k]
}
type w1 = Calc<Nodes>
type z0 = Exclude<w0,NodeA>
type z1 = Exclude<w1,NodeA>
|
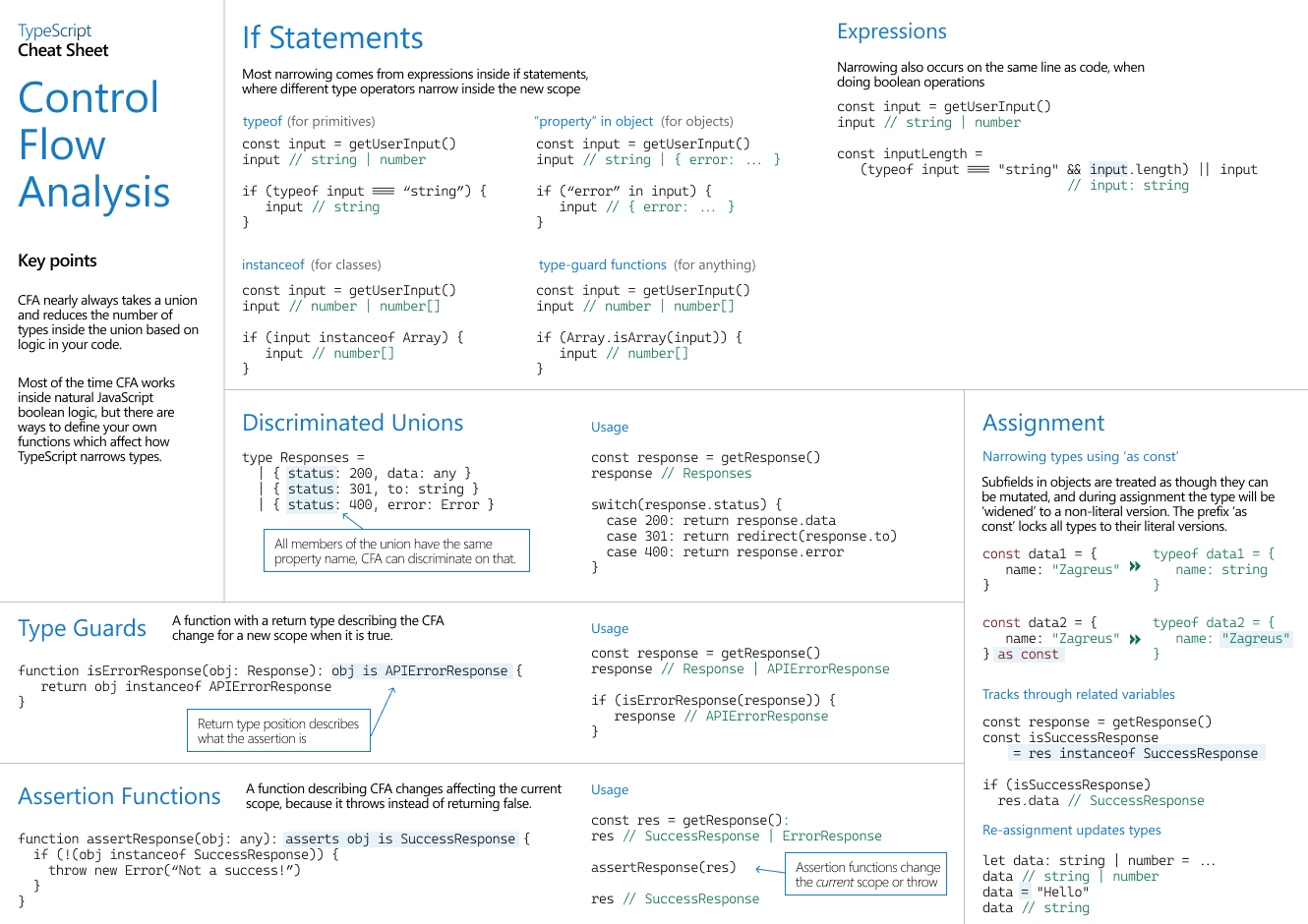
CheatSheet 图
通过if的条件自动推断 运算区间内的类型, 如 Discriminated Unions 在处理不同的服务器范围类型时
几种控制流示例
![控制流分析]()
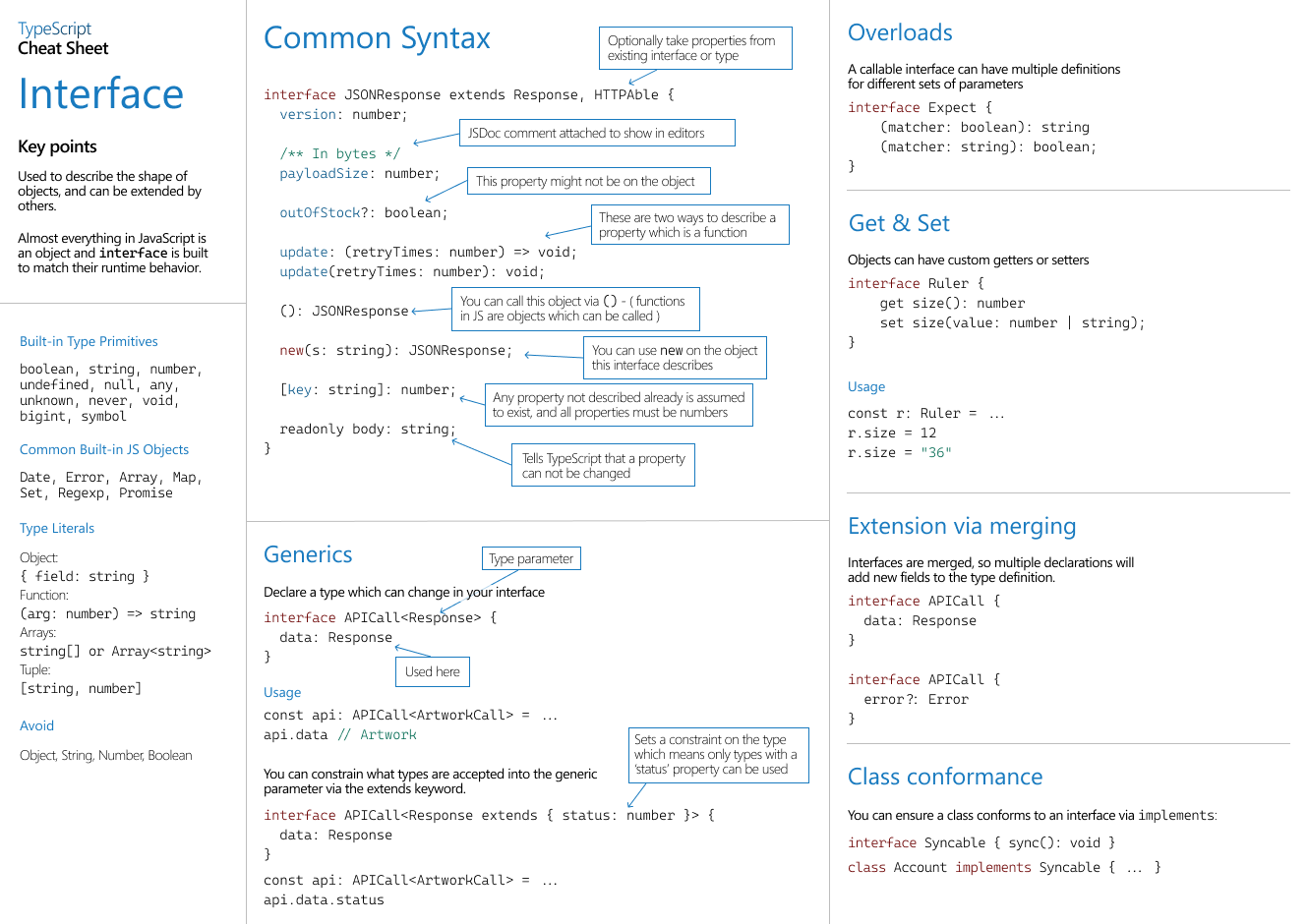
内置类型, 内置对象, 字面量, 可扩展, interface 各种写法, 限制,重载, 多处书写自动merge,写法
![接口interface]()
一个type唯一定义, 需要实例的结构和type描述完全一致,而interface 只是描述一定要的field, 写法,映射,条件推断, 模板union, 重定义名字, Tuple Type, Union,Intersecion,Type 字段索引,从数据/返回/module提取出type,
![类型type]()
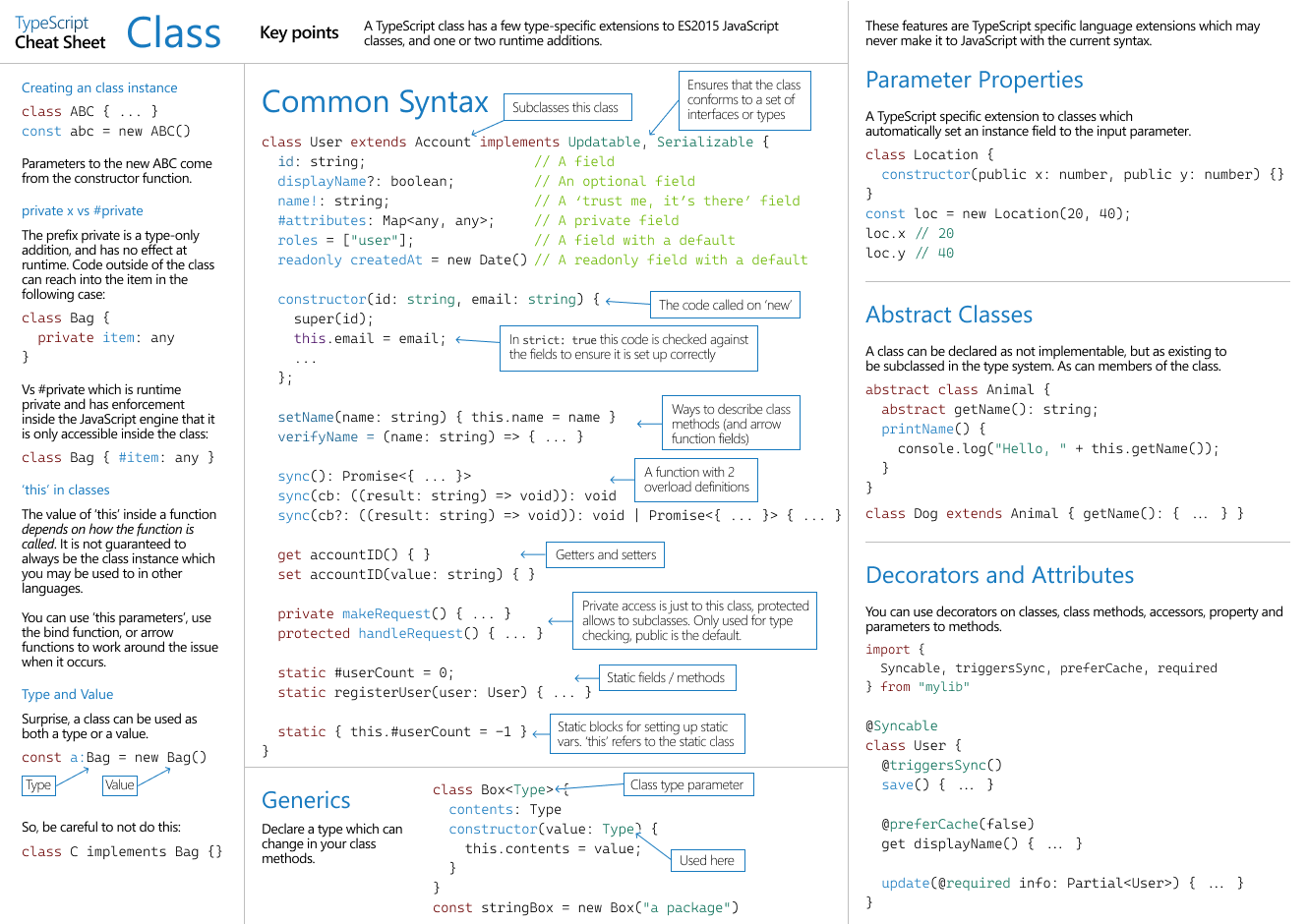
语法,Generics,虚类,构造函数,装饰器
![类class]()
Ref
antfu ts challenges
ts cheatsheets